Circular
Although circular is the new buzzword in sustainability circles, in many ways it’s a return to the way the economy operated in the distant past when most things were used for decades, repaired and reused in completely new ways. The circular economy is best described as the antidote to the traditional linear model of the ‘take, make, waste’ economy. This linear way leads to the exploitation of resources and discards them at the end of their use.

The Basics

Where To Start?

Case Study
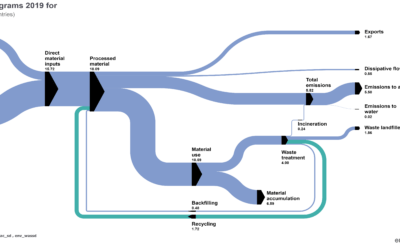
A circular economy aims to maintain the value of products, materials and resources for as long as possible by returning them into the product cycle at the end of their use, while minimising the generation of waste. Source: Eurostat
An example of this might be that a product, such as packaging, is recycled into a textile which is used to create building insulation or an item of clothing. When these reach the end of their lifespan it should then be possible to recycle them or reuse them in yet another way.
Find out more in the information and links below about the Circular Economy and what it might mean for your business.
Resources Library
How the circular economy tackles climate change
The transition to renewable energy is vital if we are to tackle climate change. Yet, with existing technologies, that transition would only tackle 55% of the emissions that cause the climate to change. To tackle the remaining 45% of emissions, which come from...
Guide to Sustainable Materials Management
This report from the OECD on Sustainable Materials Management is a comprehensive guide to the topic. It explains the need for action, the policy argument for change, and the benefits & challenges of implementing change. Case studies of various countries are given...
The $25 Trillion Opportunity
This World Economic Forum article on the economic impact of waste, on top of its environmental impact, gives an additional argument as to why we urgently need to redress our wasteful linear economy business model in favour of a circular system. The circular economy...
OECD – Circular Economy at a Glance
This report from the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) provides a clear and digestible summary of the state of its member nations in terms of circular economy progress. The issues, policy challenges, trends and environmental impact of...
Eurostat’s Guide to the Circular Economy
Eurostat (the EU Statistics Office) offers a guide to explain what the circular economy is, along with data showing the state and progress of individual EU countries in moving towards a more circular economy. Information on waste statistics are also available to show...
Circulytics – Measure the Circularity of your Business
Circulytics is a free measurement tool for businesses from the Ellen MacArthur Foundation. The assessment can measure the circularity of your business and show you where you need to improve and how. Circulytics has supported more than 1000 businesses on their journey...
Circular Economy case study: Gerrard Street Headphones
“Better stuff. Better service. Better world. This is how all devices should be designed.” Gerrard Street. Who is Gerrard Street? Gerrard Street headphones are a pioneering example of the circular economy coming to life. The Dutch company was founded in 2015 and from...
Circular Economy: where to start?
Like some other aspects of sustainable business practice, the circular economy requires you to think about your business in a very different way. It may feel very daunting to know where to start since it is a new business model and is almost like learning to speak in...
Circular Economy: the Basics
What is the Circular Economy? Circular is the new buzzword in sustainability circles. The circular economy is best described as the antidote to traditional linear production models that relies on ‘take, make, waste’ exploitation of resources without consequence for...